Understanding How Do PET Scans Work: A Comprehensive Guide to Positron Emission Tomography
#### How do PET scans work?Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are advanced imaging techniques that allow medical professionals to observe metabolic pr……
#### How do PET scans work?
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans are advanced imaging techniques that allow medical professionals to observe metabolic processes in the body. This innovative technology plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring various diseases, particularly cancers, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. In this article, we will explore how do PET scans work, their applications, benefits, and the process involved in undergoing a PET scan.
#### The Basics of PET Scans
At its core, a PET scan works by detecting gamma rays emitted from a radioactive substance injected into the patient’s body. This radioactive tracer is typically a form of glucose, which is a sugar that the body uses for energy. Since cancer cells and other abnormal tissues often have higher metabolic rates than normal cells, they absorb more of this tracer, making them visible on the PET scan.
#### The Process of a PET Scan
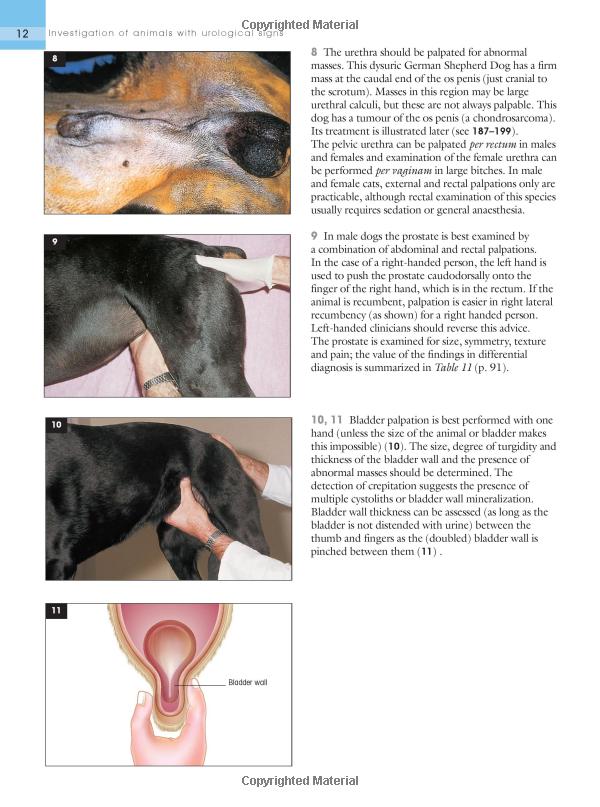
The process begins with the preparation of the patient. Before the scan, patients are usually advised to avoid eating for several hours to ensure accurate results. Once ready, a small amount of radioactive tracer is injected into a vein, usually in the arm. After the injection, patients wait for a short period to allow the tracer to circulate throughout the body and be absorbed by the tissues.
After the waiting period, patients are positioned on a comfortable table that slides into the PET scanner. The scanner itself looks similar to a large doughnut and is equipped with detectors that can capture the gamma rays emitted by the radioactive tracer. As the scanner rotates around the patient, it creates detailed images of the metabolic activity in various organs and tissues.
#### Interpreting PET Scan Results
Once the scan is complete, the images are analyzed by a radiologist, who will look for areas of increased tracer uptake, indicating higher metabolic activity. These areas may suggest the presence of tumors or other abnormalities. The results of a PET scan are often used in conjunction with other imaging techniques, such as CT or MRI scans, to provide a comprehensive view of a patient’s health.

#### Applications of PET Scans
PET scans have a wide range of applications in modern medicine. They are particularly valuable in oncology for detecting cancer, determining the extent of disease, and evaluating treatment response. In neurology, PET scans can help diagnose conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy by visualizing brain activity and metabolism. Additionally, in cardiology, PET scans can assess heart function and detect areas of reduced blood flow.
#### Benefits of PET Scans
One of the primary benefits of PET scans is their ability to provide functional imaging, allowing doctors to see how tissues and organs are functioning in real-time. This functional information is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Moreover, PET scans are non-invasive, making them a safer alternative to exploratory surgeries or more invasive diagnostic procedures.

#### Conclusion
In summary, understanding how do PET scans work is essential for both patients and healthcare providers. This technology offers invaluable insights into the body’s metabolic processes, aiding in the diagnosis and management of various medical conditions. As research and technology continue to advance, the applications and effectiveness of PET scans are expected to expand, further enhancing patient care and outcomes. Whether you are a patient preparing for a PET scan or a healthcare professional seeking to understand this imaging technique better, knowing how PET scans work can help demystify the process and underscore its importance in modern medicine.